Recently, researchers tested Google's latest video generation AI model, Veo-3, and the results showed that although the model can generate very realistic surgical videos, it has significant shortcomings in understanding medical procedures. In the study, the research team provided a surgical image and asked Veo-3 to predict what would happen in the next 8 seconds of the surgery. To do this, they created an evaluation standard called SurgVeo, which includes 50 real laparoscopic and neurosurgical videos.
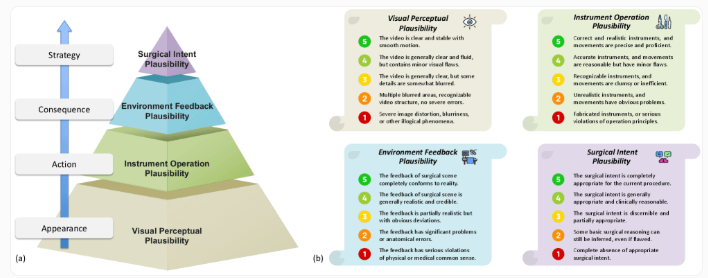
The research team invited four experienced surgeons to independently rate the AI-generated videos, with evaluation criteria covering four aspects: visual realism, reasonableness of instrument use, tissue response, and surgical logic. Although the surgeons gave high ratings to the quality of the videos generated by Veo-3, calling them "stunningly clear," in-depth analysis showed that the AI's performance in medical logic was significantly compromised. In the laparoscopic surgery test, Veo-3 scored 3.72 for visual plausibility, but only 1.78 for instrument operation, 1.64 for tissue response, and as low as 1.61 for surgical logic.
Especially in neurosurgical scenarios, Veo-3 performed even worse, with a score of only 1.13 for surgical logic after 8 seconds. The research team found that over 93% of the errors stemmed from medical logic issues, such as inventing non-existent surgical instruments and tissue responses that violated physiological laws. Attempts to provide the model with more contextual information, such as the type of surgery and specific procedural stages, did not significantly improve its performance.
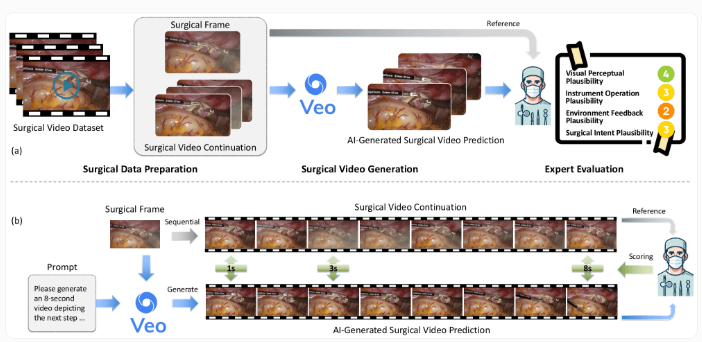
This study shows that current video generation AI is still far from truly understanding medical procedures. Although these systems may be used for doctor training and preoperative planning in the future, existing models have not yet reached a safe and reliable level of application. The research team plans to open-source the SurgVeo dataset to promote academic progress in AI's medical understanding. At the same time, it also reminds us that using such generated videos in medical training poses serious risks, potentially leading to misleading learning and incorrect surgical techniques.
Key Points:
🌟 The Veo-3 model can generate realistic surgical videos, but lacks understanding of medical logic.
🔍 Over 93% of the errors stem from medical logic problems, seriously affecting the accuracy of the videos.
📈 The research team plans to open-source the dataset to promote progress in AI's medical understanding.
