Recently, a research result from institutions including the University of Cambridge has attracted widespread attention: large language models (LLMs) not only show promise in the field of natural language processing but also bring new hope for cancer treatment. Researchers used the GPT-4 model for the first time as a tool to generate scientific hypotheses, achieving encouraging progress in the development of drugs for breast cancer.
In this study, the team aimed to find new drug combinations that could effectively combat breast cancer. They screened non-cancer drugs approved by the FDA that might have synergistic effects, setting three key principles: avoiding standard anti-cancer drugs, focusing on drugs that can target cancer cells without damaging healthy cells, and prioritizing low-cost drugs that have already received regulatory approval.
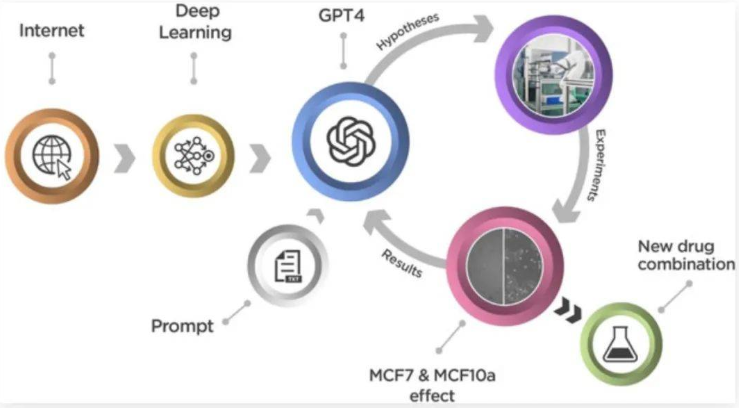
After a series of laboratory tests, researchers found that GPT-4 successfully proposed 12 groups of drug combinations, with three of them showing synergy scores higher than existing positive control drugs, demonstrating treatment effects beyond expectations. Based on the preliminary experimental results, GPT-4 further generated new drug combinations, and in four tests, it discovered another three groups with positive synergistic effects.
Notably, the combination of simvastatin and disulfiram stood out in the study. Simvastatin is a commonly used cholesterol-lowering drug, while disulfiram is mainly used to treat alcohol dependence. The study showed that these drugs, originally used to treat other diseases, may have the potential to effectively combat breast cancer. This discovery not only opens up new directions for drug development but also demonstrates the potential of large language models in scientific research.
This research result marks a major breakthrough in artificial intelligence in medical research, and it is expected to offer more treatment options for cancer patients in the future. The work of the research team provides new ideas for drug development, indicating the great potential of AI in scientific exploration. It is hoped that more scientists will be able to use this tool to contribute more innovative solutions for human health.
Paper link: https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsif.2024.0674






